Jiuzhaigou Scenic Area Case Study
Jiuzhaigou Scenic Area
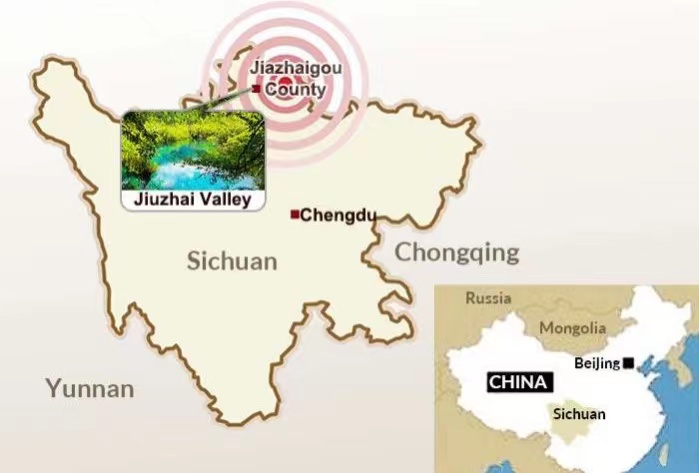
Location: North part of Sichuan province
Date established: December 15, 1978
Official name: Jiuzhaigou Conventional Protected Areas (九寨沟国家级自然保护区)
Primary Attractions:
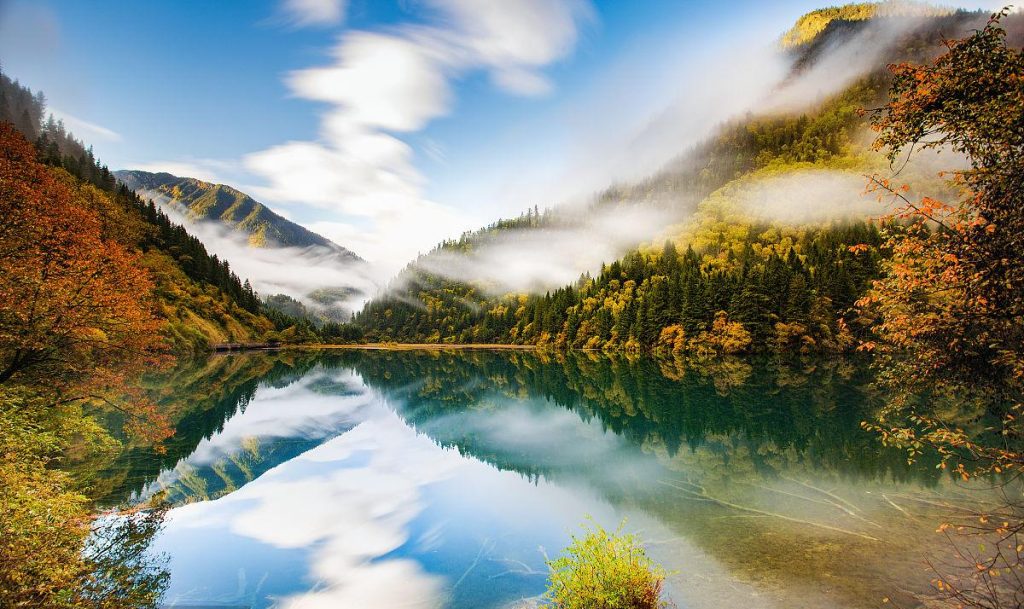
- Five Flower Lakes
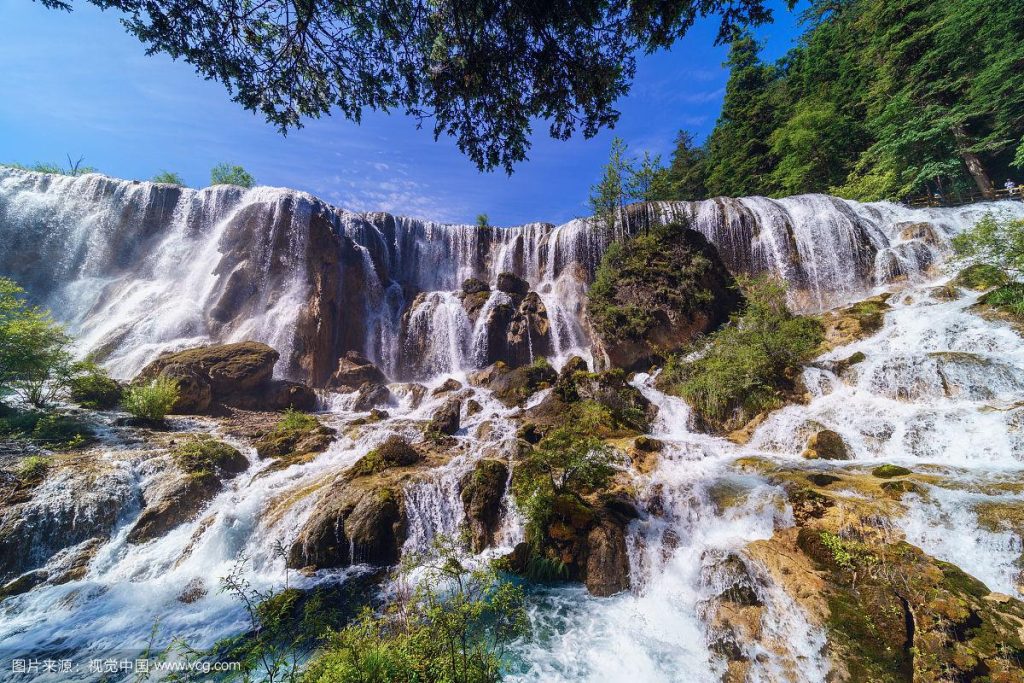
- Nuorilang Waterfall
- Five Color Pond
- Pearl Shoal Waterfall
- Mirror Lake
- Long Lake
- Panda Lake
- Primitive Forest
- ShuZheng Waterfall
Primary Wildlife:
- Giant Panda
- Golden Snub-nosed Monkey
- Duke of Bedford’s Vole
- Golden Wildebeest
- Chinese Monal


Where Jiuzhaigou is located in China?
Research Description
Title:
Vulnerability and Resilience for Risk Mitigation in Jiuzhaigou Scenic Area, China
Framework:
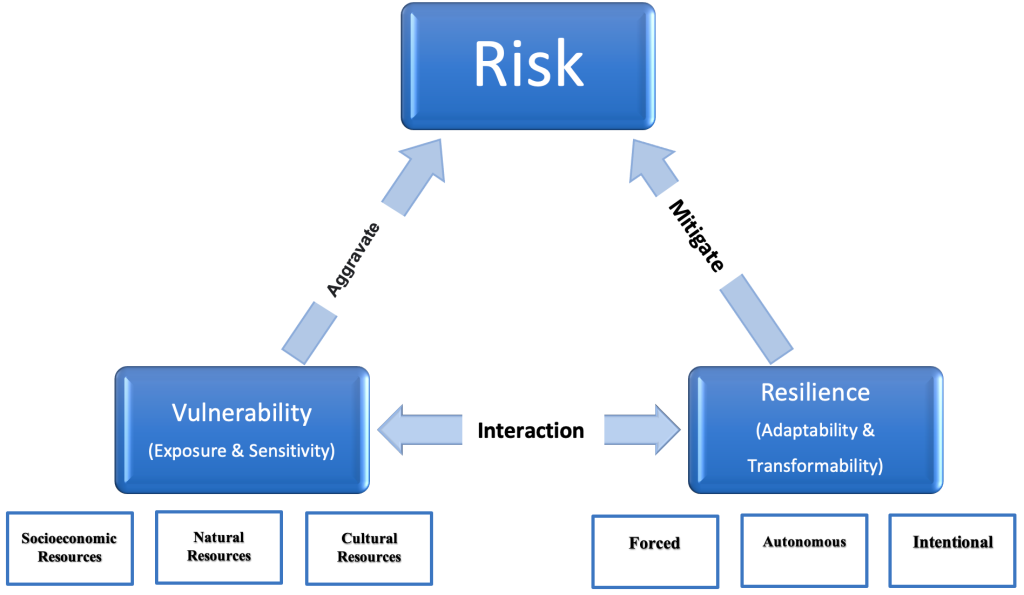
Figure 1. Managing risk through vulnerability and resilience analysis.
Research Questions:
How does vulnerability guide risk management in the Jiuzhaigou Scenic Area, particularly in terms of resilience capacity?
- What is the relationship between vulnerability, resilience, and risk?
- How have natural disasters and human crises aggravated risk for tourism systems across Jiuzhaigou Scenic Area? (based on vulnerability analysis in terms of exposure and sensitivity indices for key tourism assets)?
- How have tourism resources themselves and humans responded (intentionally, autonomously, and in a forced fashion) to recent crises or disasters in Jiuzhaigou?
- How do findings inform Jiuzhaigou risk prevention strategies moving forward?
Purpose:
The purposes of this research are to assess risks and responses associated with recent and possible future disasters / crises in Jiuzhaigou Scenic Area. Recommendations for risk prevention will be based on analyses of key tourism system vulnerabilities and adaptations / transformations over time, identifying current issues and potential risks while contributing to ongoing research in the region since 1973.
Proposed Research Timeline:
- September-December 2021 – Conduct literature review and develop research proposal
- January-March 2022 – Collect initial data and conduct fieldwork
- March-April 2022 – Analyze initial data
- April-June 2022 – Write up results in research article draft
- June-August 2022 – Revise article and submit to a peer-reviewed journal
- October 2022 – Present initial findings at Tourism Naturally Conference, Colorado State University
- Through Spring 2024 – ongoing data collection, analyses and dissemination of findings in graduate coursework, thesis, conferences, etc.
Project Lead: Yanxi Li

Li Yanxi is housed at Colorado State University, focusing on Natural Resources Tourism. Yanxi is from Chengdu, China which is famous for being the home of cute giant pandas, but also for many other natural, cultural and historical wonders. Ever since she was a kid, Yanxi has wanted to work in tourism management to help her hometown better use those tourism resources and develop more sustainably. Her current research interests center on building destination resilience against uncertain and unexpected crises or disasters that may impact people and environments around the world.
Field Expert: Dr. Lihua Li

Professor Lihua Li, Ph.D., is the director of the Mountain Tourism and Development Group for the Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, housed within the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Professor Li has been fully devoted to tourism planning, management, and research in China’s southwest mountainous areas since 1998. He has served as Deputy Director of the Tibet Autonomous Region Tourism Bureau from 2001 to 2005; Deputy Director of the Guizhou Tourism Bureau from 2007 to 2008; and the Deputy Secretary General of Administration for Liangshan Prefecture, Sichuan Province from 2016 to 2017. He has presided and participated in nearly 100 tourism planning cases in China’s southwestern mountainous areas, which include regions, towns and scenic spots. His most recent interests involve organizational reform and innovation in tourism destinations, especially in the classification and quantitative evaluation of tourism resources. From 2019-2022, Professor Li’s projects have included 1) “Tourism Poverty Alleviation Planning in Liangshan Prefecture, Sichuan” supported by the National Ministry of Culture and Tourism; 2) “Development Paths of Tourism in Northwest Sichuan” supported by the Sichuan Provincial Government; and 3) “Innovation of the Modern Governance Capacity and Systems for Jiuzhaigou’s Post-Earthquake Reconstruction and Sustainable Development”.
